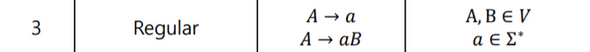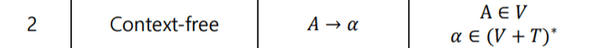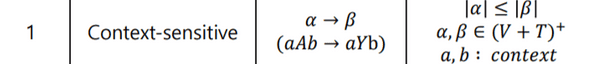NLP
-
형식언어 이론
- Context-free Grammar
- Context-sensitive Grammar
- Natural Language
문장 구조 분석
- Word-salad(말비빔): 문법적으로는 완벽히 맞지만 의미가 없는 문장
형식언어 이론 : Formal Language Theory
-
언어란?
- (형식적 측면) 유한개의 철자로 무한개의 단어와 문장을 조합한 것
- (의미적 측면) 무한한 의미를 생성할 수 있는 것
-
촘스키의 계층 구조 (Chomsky Hierarchy)
- 의미 없이 문장이 형성되는 과정을 형식으로 설명 :
형식언어(formal language theory) - groucho_grammar =
nltk.CFG.fromstring(""" V와 T로 문법 정의 """) - V :
Variable - T :
Terminal -
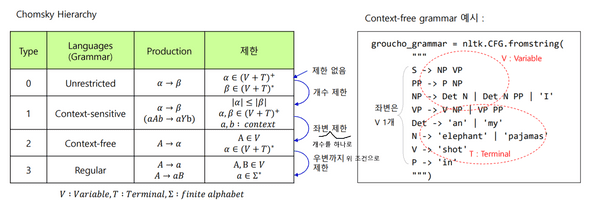
derivation: Context-free grammar에서, 우변 → 좌변(Variable, Terminal)일 때→하는 과정- Unrestricted: 자연어(사람 말)
- Context-sensitive부터 Regualr까지 오토마타(Automata)
오토마타(Automata)- 어떤 Language가 어떤 Grammar에 따르는지 그래서 Accept할지, Reject할지 Check하는 추상적인 기계(장치)
- 의미 없이 문장이 형성되는 과정을 형식으로 설명 :
-
Unrestricted(Natural Language)
-
Type-0 : Recognized by Turing Machine
Context-sensitive- Type-1 : Accepted by Linear Bound Automata
Context-free- Type-2 : Accepted by Push Down Automata (PDA)
Regular- Type-3 : Accepted by Finite State Automata (FSA)
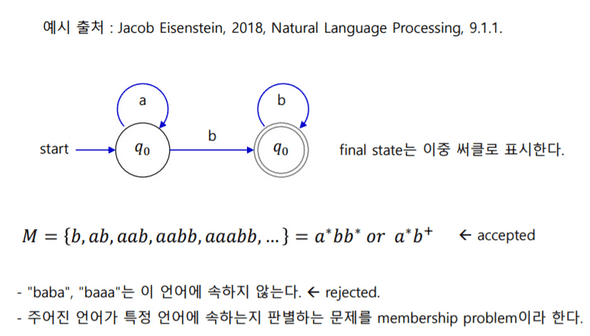
Regular Grammar
- 결정적 유한 오토마타(Deterministic finite automaton, DFA)
- Regular 언어에서 오토마타는, 어떤 게 어디 속하는지에 관한 문제인 membership porblem 판별장치
- print(FSA('aabbb')):
derivation a*b+ Automata Grammar as ->
aas ->
aaas ->
aaaaA ->
aaaabB ->
aaaabbB ->
aaaabbbS -> aS
S -> aA
A -> bB
B -> b
-S -> as | aA
A -> bB | bChomsky Hierarchy 中 Regular Grammar
- 정규언어 (Regular language) 와 유한상태 인식기 (Accepted by Finite state acceptor : FSA)
init_state = 0 final_state = [1] trap_state = 2 delta = {0: {'a':0, 'b':1}, 1: {'a':2, 'b':1}} """ {현재상태 0 {'a' 들어가면: 다음 상태는 0, 'b' 들어가면: 다음 상태는 1}} {현재상태 1 {'a' 들어가면: 다음 상태는 2, 'b' 들어가면: 다음 상태는 1}} """ def FSA(string): state = init_state # 초기상태 = 0 for s in string: # 'a' 들어가고 'a' 들어가고 'b' 들어가는 등 하나씩 for문에 입력됨! state = delta[state][s] if state == trap_state: # state가 2가 되면 멈춤. 즉, 1상태에서 'a'가 들어오면 멈춤 # 즉, 문자열을 읽어가다가 trap state에 빠지면 reject 됨 break return state in final_state # state값이 final_state에 있으면 True, 없으면 False print(FSA('aabbb')) # True print(FSA('aabba')) # False print(FSA('aabbc')) # error print(FSA('a')) # False
Context-free Grammar
-
Accepted by Push Down Automata, PDA
- {a의 n승 b의 n승, n>=1}가 aaaabbbb라는 오토마타 형태(뭐다음 뭐 나와야 하고, 뭐 다음 뭐 나와야 하는 것)을 기계는 기억하지 못함. ex: N의 n승 N의 n승 -> the cat(N) the dog(N) chased(V) run(V)
-
이때, 과거 데이터를 기억하는 오토마타의 장치: Stack
Chomsky Hierarchy 中 Context-free Grammar
Context-sensitive Grammar
-
좌우 문맥에 따라 달라지는 경우
- S -> NP VP
- aSb -> NP VP
- cSd -> NP PP
- aSb -> aS by
- bSa -> aA bb
- Accepted by Linear Bound Automata
-
'한글모아쓰기'에 활용되기도 함
Chomsky Hierarchy 中 Context-sensitive Grammar
Unrestricted Grammar (Natural Language)
- Recognized by Turing Machine
- 의미는 틀려도 되고, 아무 단어나 막 조합해도 되는 것
-
참고:
- 아마추어 퀀트, blog.naver.com/chunjein
- 코드 출처: 크리슈나 바브사 외. 2019.01.31. 자연어 처리 쿡북 with 파이썬 [파이썬으로 NLP를 구현하는 60여 가지 레시피]. 에이콘